Smart Manufacturing Engineering
Manufacturing continues to remain one of the leading contributors to the national GDP, and the growth and innovation within nearly all sectors of manufacturing can be attributed to data-driven solutions. Smart or intelligent manufacturing technologies being applied to increase productivity, improve quality, and reduce costs include digital engineering/design/manufacturing, robotics and automation, real-time data analytics, lean and agile process management, six sigma statistical process control, and additive manufacturing. Smarter, automated and more flexible companies need academically qualified and skilled manufacturing engineers.
Learning Outcomes
Graduates of the Smart Manufacturing Engineering program will be able to:
- Identify, formulate, and solve complex engineering problems by applying principles to engineering, science and mathematics;
- Apply engineering design to produce solutions that meet specified needs with consideration of public health, safety, and welfare, as well as global, cultural, social, environmental and economic factors;
- Communicate effectively with a range of audiences;
- Recognize ethical and professional responsibilities in engineering situations and make informed judgements, which must consider the impact of engineering solutions in global, economics, environmental, and societal contexts;
- Function effectively on a team whose members together provide leadership, create a collective and inclusive environment, establish goals, plan tasks, and meet objectives;
- Develop and conduct appropriate experimentation, analyze and interpret data, and use engineering judgement to draw conclusions;
- Acquire and apply new knowledge as needed, using appropriate learning strategies.
Employment Opportunities
Graduates typically work as manufacturing engineers in areas such as product and process development and design, quality control, advanced manufacturing, lean manufacturing, systems design and integrator, process and plant-facilities design, project management, and industrial engineering. After gaining industrial experience, graduates often move into organizational management positions. Graduates are also prepared to continue their education at the graduate level. Graduating seniors are encouraged to take the Fundamentals of Engineering examination, which is the first of two examinations that lead to becoming a licensed professional engineer.
Your job description may include:
- Design automated manufacturing plants, systems and material-handling solutions
- Detailed engineering design and collaboration with 3rd parties on system build, installation, commissioning,
- Scheduling and planning
- Process engineering
- Six Sigma and quality control
- Project management
Your employer may be:
- Tesla
- GE
- Proctor and Gamble
- Swagelok
- Lilly
- Mitsubishi
Smart Manufacturing Engineering Curriculum
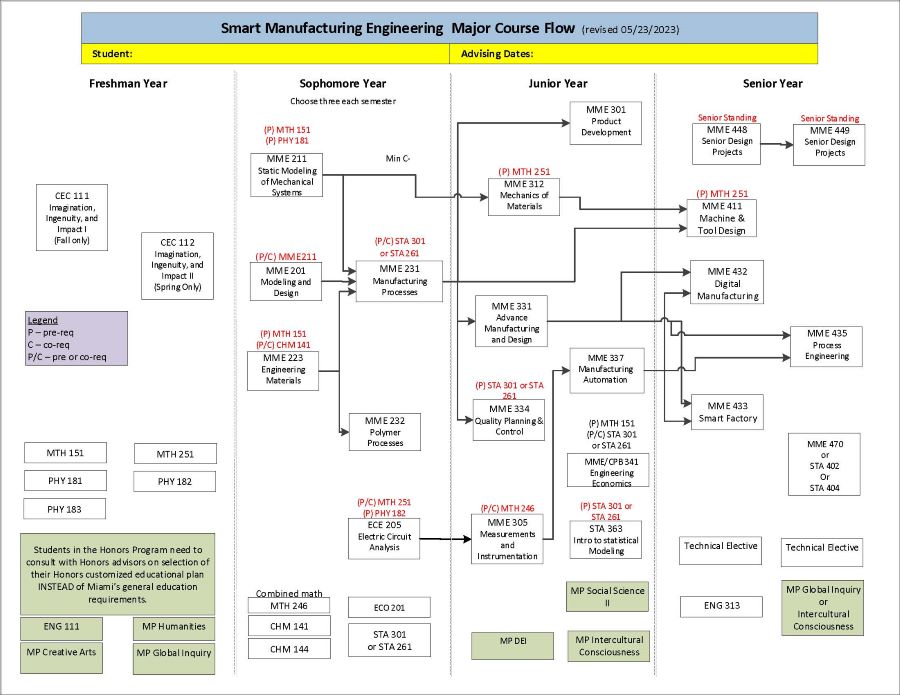
Textual Description of Smart Manufacturing Engineering Course Flowchart 2023-24
This chart shows the courses needed to graduate, when those courses are typically taken, and the order in which the courses must be taken. The main area of the chart shows four boxes, one each for first-year, sophomore, junior, and senior years. Within each year, classes are shown in roughly two columns representing fall then spring semester. Courses are listed within each semester to indicate when the course is typically taken. An arrow leaving a course and pointing to another course indicates that the first course must be taken prior to taking the second course. Below all the years is a section containing a collection of courses that can be taken when convenient for the student and therefore no particular semester is recommended. All students may have some variation in degree plans, be sure to be communication with your academic advisor.
Fall semester (17 credit hours)
- Calculus I; MTH 151 (5 hrs)
- Is a pre-requisite for MTH 251, MME 223, MME 211, and MME 202.
- Is a pre-requisite or co-requisite of PHY 191.
- Physics I; PHY 191 (5 hrs)
- Is a pre-requisite for PHY 192 and MME 211.
- Requires a pre-requisite or co-requisite of MTH 151.
- Computing, Engineering, and Society; CEC 101 (1 hr)
- Composition & Rhetoric ENG 109 (4 hrs) or ENG 111 (3 hrs ; GMP English)
- ENG 109 is an adaptation of ENG 111 for non-native English speakers.
- 1 Miami Plan Creative Arts Course
Spring semester (18 credit hours)
- Calculus II; MTH 251 (4 hrs)
- Is a pre-requisite for MTH 252, MTH 246, ECE 205, MME 311, MME 312, MME/CPB313, and MME 314.
- Requires a pre-requisite of a C or better in MTH 151.
- Physics II; PHY 192 (5 hrs)
- Is a pre-requisite for ECE 205.
- Requires a pre-requisite of PHY 191.
- Introduction to MME; MME 102 (3 hrs)
- Is a pre-requisite for MME 202 and MME 201 as well as a pre/co-requisite for MME 211.
- 1 Miami Plan Humanities Course
- 1 Miami Plan Global Course
Fall semester (17 credit hours)
- Chemistry I with Chemistry I lab; CHM 141 & CHM 144 (5 hrs)
- Must be taken simultaneously.
- Is a pre/co-requisite for MME 231 as well as a pre-requisite for MME 314.
- Calculus III; MTH 252 (4 hrs)
- Is a pre-requisite for MME 313 as well as a pre/co-requisite of MME 321.
- Requires a pre-requisite of MTH 251.
- Engineering Materials; MME 223 (3 hrs)
- Is a pre-requisite for MME 231.
- Requires a pre-requisite of MTH 151 as well as pre/co-requisite of MME 223.
- Static Modeling of Mechanical Systems; MME 211 (3 hrs)
- Is a pre-requisite for MME 313, MME 311, MME 231, MME 312, MME 314, and MME 321.
- Must complete with a C- or better.
- Requires pre-requisites of MTH 151 and PHY 191 as well as a pre/co-requisite of MME 102.
- Modeling and Design; MME 201 (2 hrs)
- Is a pre-requisite for MME 231, and MME 311.
- Requires a pre/co-requisite of MME 211.
Spring semester (17-18 credit hours)
- Statistics; STA 261 (4 hrs) (no prerequisite) or STA 301 (3 hrs)
- STA 301 requires a pre-requisite of MTH 151.
- Is a pre/co-requisite for MME 231 and MME 341.
- Manufacturing Processes; MME 231 (3 hrs)
- Is a pre-requisite for MME 411.
- Requires pre-requisites of MME 201, MME 211, MME.
- Microeconomics; ECO 201 (3 hrs)
- Also counts towards the GMP Social Science foundation in the Miami Plan.
- Differential Equations and Linear Algebra; MTH 246 (4 hrs)
- Is a pre-requisite for MME 321 and MME 403 as well as a pre/co-requisite for MME 202 and MME 305.
- Requires a pre-requisite of MTH 251.
- Electric Circuit Analysis; ECE 205 (4 hrs)
- Is a pre-requisite for MME 305.
- Requires a pre-requisite of PHY 192 as well as pre/co-requisite of MTH 251.
Fall semester (15 credit hours)
- Product Development; MME 301 (3 hrs)
- Requires pre-requisites of MME 201 and MME 231.
- Dynamic Modeling of Mechanical Systems; MME 311 (3 hrs)
- Requires pre-requisites of MTH 251, MME201, and MME 211.
- Fluid Mechanics; MME/CPB 313 (3 hrs)
- Is a pre-requisite for MME 403 and MME 415.
- Requires pre-requisites of MME 211, MTH 252, and PHY 191.
- Measurements and Instrumentation; MME 305 (3 hrs)
- Is a pre/co-requisite for MME 321.
- Requires a pre-requisite of ECE 205 as well as pre/co-requisite of MTH 246.
- Technical Writing ENG 313 (3 hrs; GMP Advanced Writing)
- Requires a pre-requisite of ENG 109 or ENG 111.
Spring semester (15 credit hours)
- Quality Planning & Control; MME 334 (3 hrs)
- Requires pre-requisites of STA 301/261 and MME 231.
- Mechanics of Materials; MME 312 (3 hrs)
- Is a pre-requisite for MME 411.
- Requires a pre-requisite of a C- or better in MME 211.
- Engineering Thermodynamics; MME/CPB 314 (3 hrs)
- Is a pre-requisite for MME 403 and MME 415.
- Requires pre-requisites of MME 211, PHY 191, CHM 141, and MTH 251.
- Engineering Economics; MME/CPB 341 (3 hrs)
- Requires pre-requisites of MTH 151, and MME 102 as well as a pre/co-requisite of STA301/261.
- 1 Miami Plan Intercultural Perspective Course
Fall semester (14-15 credit hours)
- Senior Design Projects; MME 448 (2 hrs; GMP Capstone)
- Requires senior standing in order to enroll.
- Manufacturing Design; MME 434 (3 hrs; MFG track)
- Requires a pre-requisite of MME 231.
- Manufacturing Competitiveness; MME 435 (3 hrs)
- Requires a pre-requisite of MME 231.
- Only offered in Fall semesters.
- Technical Elective 1
- For Manufacturing Engineering Majors, you must choose two technical electives to pursue. For options, please consult:https://bulletin.miamioh.edu/engineering-computing/smart-manufacturing-bse/ or your academic advisor.
- 1 Miami Plan Biological Science
Spring semester (15 credit hours)
- Senior Design Projects: MME 449 (2 hrs; GMP Capstone)
- Second semester of senior design, requires MME 448 and senior standing.
- Manufacturing Automation; MME 437 (3 hrs; MFG Track)
- Requires pre-requisites of MME 231 and MME 305.
- Machine & Tool Design; MME 411 (4 hrs)
- Requires pre-requisites of MTH 251, MME 231, and MME 312.
- Technical Elective 2
- For Manufacturing Engineering Majors, you must choose two technical electives to pursue. For options, please consult: https://bulletin.miamioh.edu/engineering-computing/smart-manufacturing-bse/ or your academic advisor.
- 1 Miami Plan Global Course